

The nucleotide came into existence when a phosphate group binds to the C-5 of sugar present in the nucleoside. The most widely recognized site of esterification and phosphate group attachment is usually the C-5 OH group of the pentose sugar. The nitrogenous base is placed over the plane of pentose sugar when the design is viewed from a standard direction and orientation this type of N-glycosidic linkage arrangement is referred to as β.Ī nucleotide is a nucleoside that is at least joined to one phosphate group through an ester linkage. The N-1 of a pyrimidine or N-9 of a purine is connected to C-1 of sugar. Since it is not present in RNA, so no need to write deoxy as prefix). The RNA contains four types of nucleoside units, namely:Ĭytidine, uridine, guanosine, and adenosine, while those in DNA are called deoxycytidine, deoxyguanosine, deoxyadenosine, and thymidine (Yes, Thymidine, you heard it right. The smallest unit comprising of a base attached to a pentose sugar is alluded to as a nucleoside. Primary structural Insights: The nucleic acids offer 3-D details on nucleotide base pairing, structure, and various other essential aspects of DNA and RNA. To know more about nucleotides click here Molecular structure of DNA Two of the nucleotide bases are derived from purine guanine (G) and adenine (A), while the other two from pyrimidine uracil (U, RNA just) or thymine (T, DNA just) and cytosine (C).
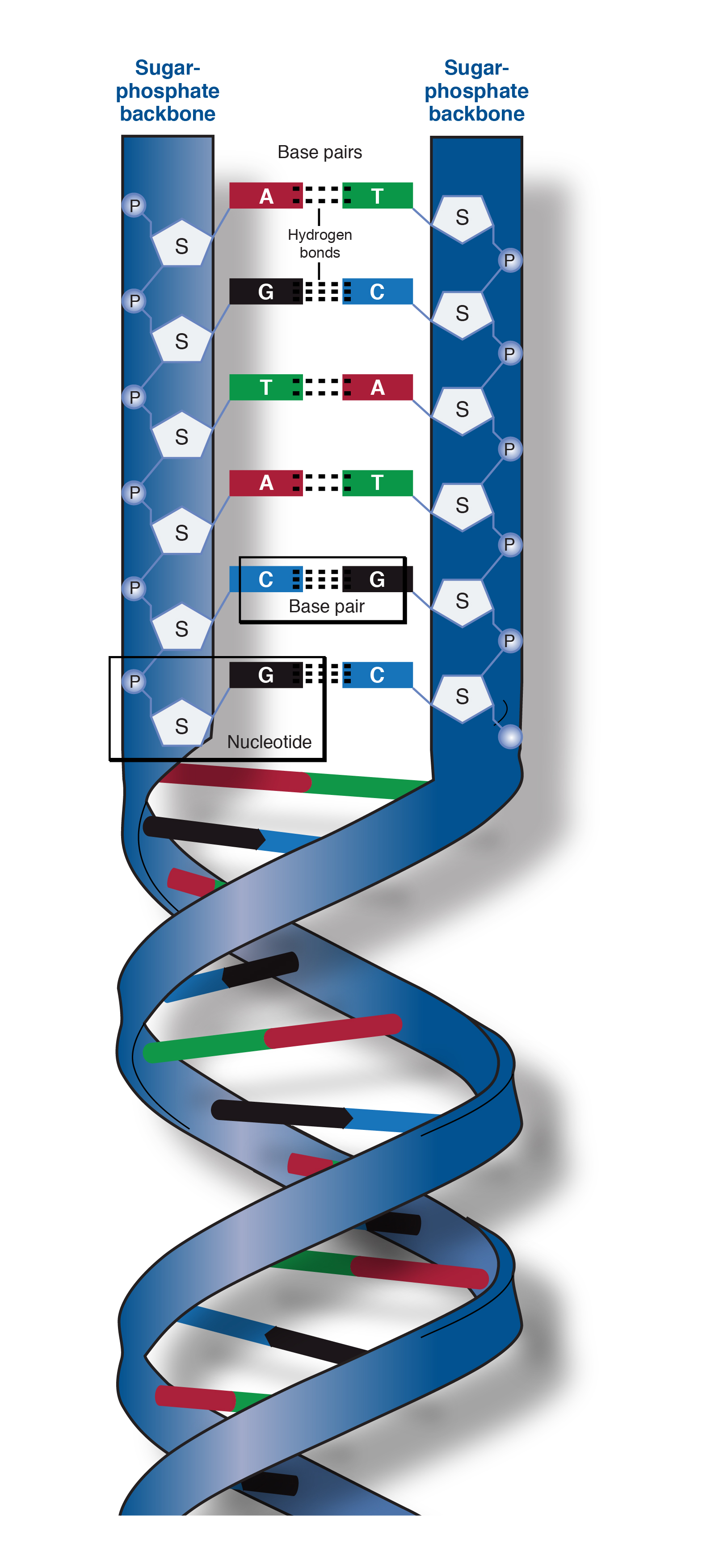
Though the sugar-phosphate backbone is consistent in DNA and RNA, the nucleotide bases vary from one monomer to the next. The chain of sugars connected by phosphodiester linkages is considered as the Nucleic acid backbone. In particular, the 3’ hydroxyl (3 – OH) group of the ribose sugar of one nucleotide forms an ester bond with the phosphate, this phosphate group is also bonded to the 5’ OH group of the adjacent ribose sugar of the neighboring nucleotide. The pentose sugars in nucleic acids are bound to each other by phosphodiester linkages.įigure: Structure of Ribose and Deoxyribose sugar found in RNA and DNA respectively Its prefix deoxy demonstrates that the 2’ carbon atom of the deoxyribose sugar does not have the oxygen atom that is present with the 2’ carbon molecule of ribose sugar (the sugar in ribonucleic acid, or RNA), as displayed in the figure below. The pentose sugar deoxyribose is present in DNA structure (deoxyribonucleic acid). Simple stem-loop structure is observed when a nucleic acid has complementary sequences within the molecule and forms intra-molecular base pairing to form double-helical structures from a single nucleic acid molecule.The replication process is referred to as a semiconservative for DNA.Erwin Chargaff proposed that the proportions of guanine to cytosine and of adenine to thymine were almost something similar in all species taken into consideration.The nucleotide base pairing outcomes in arranging the DNA into a two-strand helical structure.None of the ends is linked to another nucleotide. The opposite terminal or end has a 3 – Hydroxyl group.
#Sugar phosphate backbone ester free


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
